Smart Contracts: The Future of Contract Management Explained
Contracts are an essential part of any business transaction. They help define the terms and conditions of a deal, ensure that both parties understand their obligations, and protect the interests of all involved. However, traditional contract management can be a tedious and time-consuming process, often involving numerous intermediaries and manual tasks. That’s where smart contracts come in.
Smart contracts are self-executing digital contracts that use blockchain technology to automate the process of contract management. They are designed to be secure, transparent, and tamper-proof, ensuring that all parties involved can trust in the validity of the contract. In this article, we’ll explore the potential of smart contracts and their impact on the future of contract management.
Table Of Contents
- What are Smart Contracts?
- Most Popular Smart Contract Platforms
- Advantages of Smart Contracts
- Applications of Smart Contracts
- Limitations of Smart Contracts
- Smart Contract Development
- Smart Contract Security
- Smart Contract Verification
- Smart Contract Governance
- Smart Contract Tokens
- Smart Contract Insurance
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What are Smart Contracts?
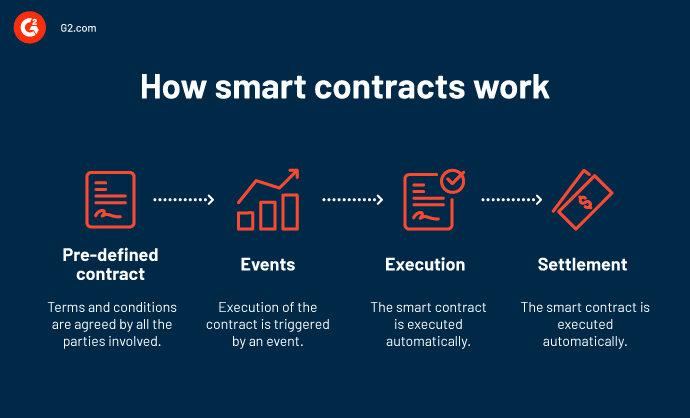
Smart contracts are computer programs that automatically execute the terms of a contract when certain conditions are met. They are built on blockchain technology, which allows for secure and transparent transactions between parties without the need for intermediaries.
Smart contracts are written in programming languages, such as Solidity, and stored on the blockchain. They are triggered by specific events or actions, such as the completion of a task or the transfer of funds, and can execute automatically without the need for human intervention.
The technology has evolved beyond Bitcoin and can be used for many different purposes, such as in real estate transactions, corporate governance, and healthcare.
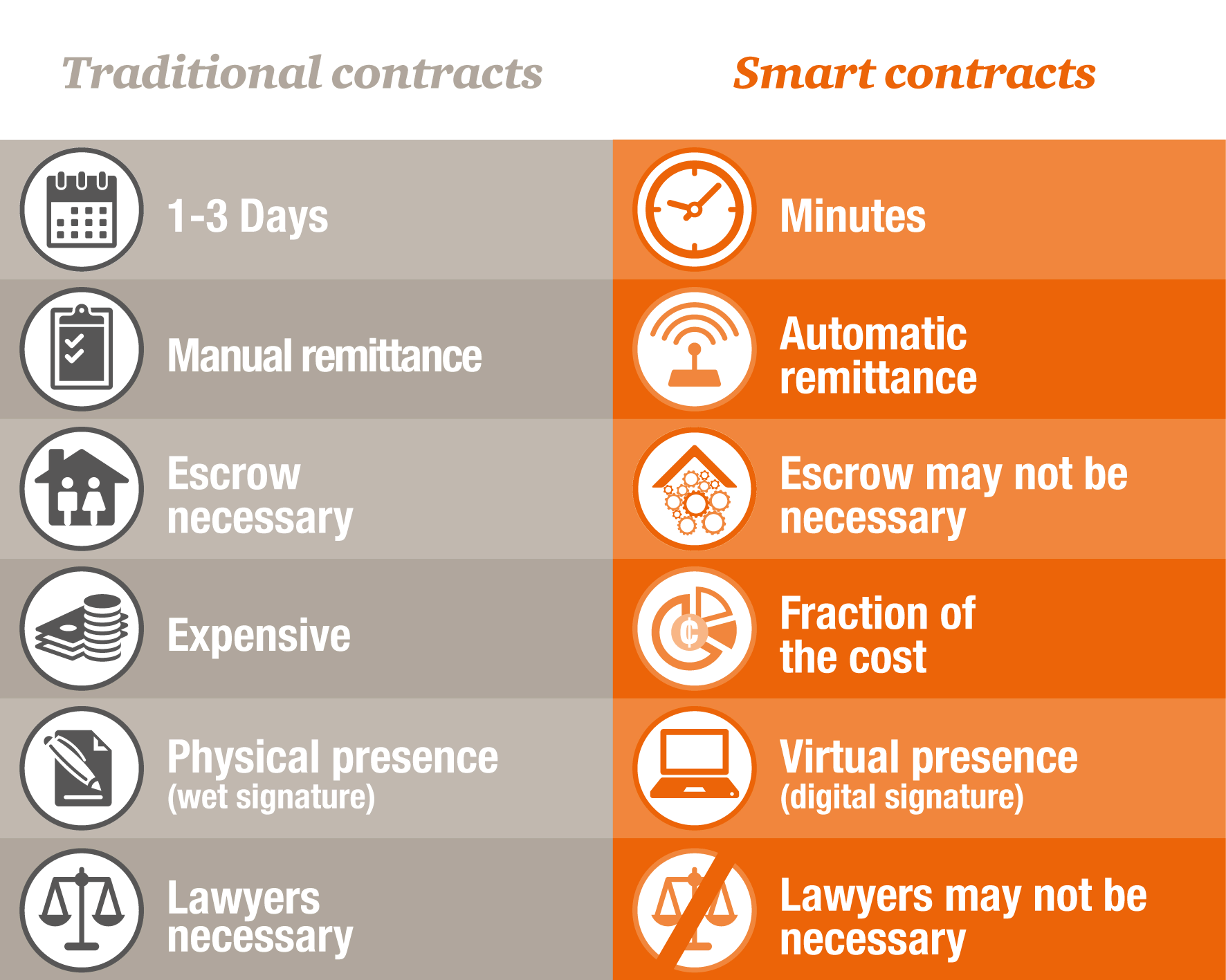
There are many benefits associated with smart contracts, including efficiency, accuracy, and immutability. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers and banks, resulting in cost savings and increased speed of execution.
Also, they are transparent, and all parties can view the terms of the contract, ensuring that there is no ambiguity or confusion. They are also immutable, meaning that once they are executed, they cannot be changed, providing security and preventing fraud.
Most Popular Smart Contract Platforms
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are programmed to automatically execute when specific conditions are met. There are several platforms that support the development and deployment of smart contracts.
Here are some of the most popular smart contract platforms:
1. Ethereum – Ethereum is the most widely used platform for creating and deploying smart contracts. It is an open-source blockchain platform that enables developers to build decentralized applications using smart contracts. Ethereum has its own programming language called Solidity, which is used to write smart contracts.
2. EOS – EOS is a blockchain-based platform that is designed for the development and deployment of decentralized applications. It is known for its high transaction speeds and scalability, which makes it an ideal platform for the creation of smart contracts.
3. TRON – TRON is a blockchain-based platform that is focused on the entertainment industry. It is designed to enable the creation of decentralized applications that can be used to share and distribute digital content. TRON supports the creation and deployment of smart contracts using its own programming language called Solidity++.
4. Hyperledger Fabric – Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source blockchain platform that is designed for the development and deployment of enterprise-grade applications. It is known for its scalability, security, and flexibility, which makes it an ideal platform for the creation of smart contracts.
5. R3 Corda – R3 Corda is a distributed ledger platform that is designed for the financial industry. It is used for the creation and deployment of smart contracts that are designed to automate financial transactions between multiple parties.
In conclusion, these are some of the most popular smart contract platforms that are used by developers and businesses around the world. Each platform has its own unique features and benefits, which makes it important to choose the right platform based on the specific needs of the project.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer several advantages over traditional contract management, including:
1. Efficiency: Smart contracts automate many of the tasks involved in contract management, reducing the time and effort required to execute a contract.
2. Transparency: Smart contracts are stored on a public blockchain, making them transparent and easily accessible to all parties involved.
3. Security: Smart contracts are tamper-proof and can only be executed when certain conditions are met, ensuring that all parties involved can trust in the validity of the contract.
4. Cost Savings: Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as lawyers and brokers, reducing the overall cost of contract management.
5. Speed: Smart contracts can be executed in real-time, reducing the time it takes to finalize a contract.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have the potential to transform a wide range of industries, including:
1. Real Estate: Smart contracts can be used to automate the process of buying and selling property, reducing the time and cost involved in real estate transactions.
2. Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts can be used to track the movement of goods and ensure that all parties involved in the supply chain are meeting their obligations.
3. Finance: Smart contracts can be used to automate the process of lending and borrowing money, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing the speed and efficiency of financial transactions.
4. Insurance: Smart contracts can be used to automate the claims process, reducing the time and cost involved in processing claims.

Limitations of Smart Contracts
While smart contracts offer many advantages, there are also some limitations to consider, including:
1. Complexity: Smart contracts can be complex to develop and require a high level of technical expertise.
2. Immutability: Once a smart contract is executed, it cannot be changed, even if there are errors or mistakes in the contract.
3. Legal Recognition: Smart contracts are not yet legally recognized in many jurisdictions, which could create challenges for businesses operating in those regions.
Smart Contract Development
Smart contract development involves writing and testing the code for a smart contract. The process typically involves the following steps:
1. Defining the Contract: The first step in smart contract development is to define the terms and conditions of the contract.
2. Writing the Code: The next step is to write the code for the smart contract, using a programming language such as Solidity.
3. Testing the Contract: Once the code is written, it needs to be tested to ensure that it works as intended.
4. Deploying the Contract: Once the contract has been tested, it can be deployed to the blockchain.

Smart Contract Security
Smart contract security is critical to ensuring the integrity of the contract. There are several best practices that developers can follow to ensure that their smart contracts are secure, including:
1. Code Review: Smart contract code should be reviewed by multiple developers to ensure that it is free from vulnerabilities.
2. Testing: Smart contracts should be thoroughly tested to identify any security weaknesses.
3. Auditing: Smart contracts should be audited by third-party security experts to identify any potential security issues.
Smart Contract Verification
Smart contract verification involves verifying the code of a smart contract to ensure that it is free from vulnerabilities. There are several tools and services available that can help with smart contract verification, including:
1. MythX: MythX is a security analysis platform that uses symbolic execution to identify vulnerabilities in smart contract code.
2. SmartCheck: SmartCheck is a tool that checks smart contract codes for common security issues.
3. CertiK: CertiK is a blockchain security company that provides smart contract auditing and verification services.

Smart Contract Governance
Smart contract governance involves establishing rules and procedures for the management and execution of smart contracts. This can include establishing a governance structure, defining roles and responsibilities, and setting policies for contract execution.
Smart Contract Tokens
Smart contract tokens are digital tokens that are created and managed using smart contracts. They can be used for a wide range of purposes, including:
1. Cryptocurrencies: Smart contract tokens can be used as cryptocurrencies, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries.
2. Utility Tokens: Smart contract tokens can be used as utility tokens, providing access to a specific service or product.
3. Security Tokens: Smart contract tokens can be used as security tokens, representing ownership in an asset or company.

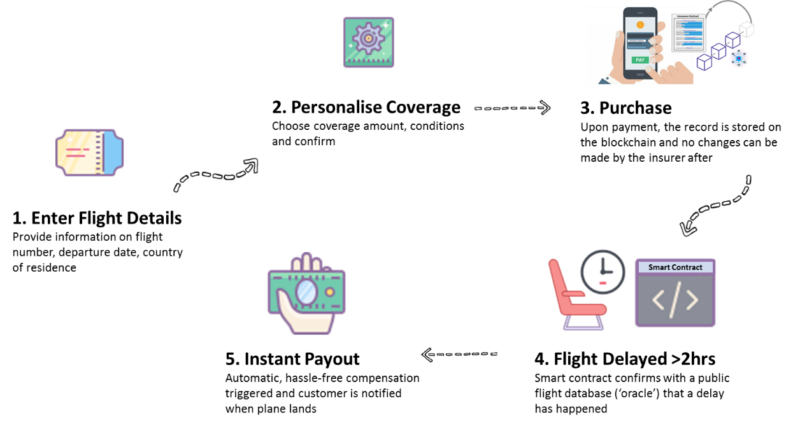
Smart Contract Insurance
Smart Contract Insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides coverage against financial losses resulting from errors or vulnerabilities in smart contracts. It is designed to protect individuals and businesses that use smart contracts from the potential risks associated with their use.
Smart Contract Insurance works by providing customized coverage that is tailored to meet the specific needs of the contract in question, such as the value of the contract and the type of transaction involved.
Here are some key points about Smart Contract Insurance:
► Smart Contract Insurance protects against financial losses resulting from coding errors, hacking, or other vulnerabilities in the smart contract code.
► This type of insurance provides peace of mind to businesses and individuals that rely on smart contracts for critical business processes or transactions.
► The premium for Smart Contract Insurance is based on the level of risk involved, which is determined by factors such as the complexity of the contract and the value of the transaction.
► Smart Contract Insurance promotes trust and confidence in the use of smart contracts, encouraging greater adoption of this technology.
► This type of insurance is likely to become increasingly important as the use of smart contracts continues to grow.
In conclusion, Smart Contract Insurance is an innovative insurance product that provides protection and peace of mind to businesses and individuals that use smart contracts. It offers customized coverage that is tailored to meet the specific needs of the contract in question and promotes trust and confidence in the use of this technology.
FAQs
Q1. What is the difference between a traditional contract and a smart contract?
A. Traditional contracts are paper-based agreements that require intermediaries and manual processes to manage. Smart contracts are digital contracts that use blockchain technology to automate the process of contract management.
Q2. Are smart contracts legally binding?
A. In many jurisdictions, smart contracts are not yet legally recognized. However, the legal recognition of smart contracts is evolving, and they are becoming increasingly accepted as legally binding agreements.
Q3. Can smart contracts be changed once they are executed?
A. No, smart contracts are immutable, meaning that once they are executed, they cannot be changed.
Conclusion
As blockchain technology continues to develop, smart contracts are becoming increasingly popular and widely used. With the rise of decentralized applications and the growing adoption of cryptocurrencies, the market for smart contracts is expected to continue to grow.
It is important for businesses and individuals to understand the potential benefits and limitations of this technology. While there are some risks involved, the benefits of smart contracts are significant, and they have the potential to transform the way contracts are managed and executed.
In conclusion, smart contracts are the future of contract management, offering numerous advantages over traditional contract management. While there are some limitations to consider, the benefits of smart contracts make them a promising technology for the future.